Mealtime Partners, Inc.
Specializing in Assistive Dining and Drinking Equipment
January 2018 Independent Eating and Drinking Newsletter

|
January Topics:
|
||
|
Mealtime Partners Home Page Send a Comment or Suggestion |
|||
| Subscribe to Newsletters |
New Terminologies Associated with Food Textures
In the past, the terminologies used to describe the levels of food and liquid modification necessary for individuals who are diagnosed with dysphagia varied significantly throughout the world. It was therefore desirable to create terminologies that could be used and understood globally. The International Dysphagia Diet Standardization Initiative (IDDSI) was established to develop global standardized terminology and definitions for texture modified foods and thickened liquids.
The IDDSI developed a 7-point framework illustrated in the following chart:
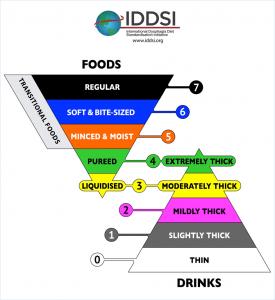
This article will discuss the preparation of foods using the texture terminologies described in this chart.
Regular Food: As the name implies, regular food has no modification made to it. It is standard table food that can be found in a home or restaurant. The food might need to be cut up into manageable sized pieces, but that is to assist someone with manual dexterity issues rather than chewing or swallowing issues. A caveat to this discussion is that tough meat is difficult for anyone to eat and, therefore, it should be tenderized, if possible, and cut into small pieces to make it easier to eat.
Soft and Bite Sized: It is important that all food that is offered to someone who should eat a soft, bite sized diet is moist and tender. Vegetables like green beans should not be stringy. Food should be cut into 1/4 inch cubes or less. Typically, food fragments should be no bigger than a green pea. Even though the food should be moist, the food should not consist of liquids and solids, like soup, because mixed textures can be difficult to process in the mouth. Lumps are easily tracked as to their position in the mouth while the liquid can move around in an uncontrolled manner and move to the back of the throat and cause choking. Finger foods should be avoided.
Minced and Moist: This category of food texture is often referred to as “ground”. The food is processed in a blender to be a similar texture to cottage cheese or ground beef. For most food types, liquids will need to be added as the food is ground up to make it moist enough to be easy to eat. Depending upon the dietary requirements for the individual, broth, butter, cream, milk or sour cream can be used to moisten the food. Also, food that is minced often loses its original flavor and can taste bland. Under these circumstances, flavor can be added by using one of the many non-salt based flavors that can be found in the condiments isle of the grocery store (e.g., Lawry's salt-free seasonings, or any of the McCormick or Weber seasonings). Also, some people enjoy the “feel” of hot sauce on their food. For people who have a poor sense of taste, food is more felt than tasted and thus hot sauce provides an enjoyable sensation.
Pureed: Pureed food is blended in the same way that minced food is prepared. However, more liquid is added to the food and the blending process takes a longer time. Blending should continue until the food no longer has any lumps or texture remaining in it. Liquid will need to be added to the food to allow it to be blended into a smooth texture with all of the lumps removed. When food is pureed, it should have the texture of pudding. It will be the same thickness as liquids that are thickened to a "pudding thick" consistency. The puree stage of food texture and the extremely thick stage of liquid thickness are equal.
Liquidised: As with pureed food, liquidised foods are comparable with liquids that have been thickened to “honey-thick” consistency. A significant amount of liquid will need to be added to the food to allow it to adopt a liquidised texture. Like pureed foods, liquidised foods should be flavored adequately to make them appealing to the consumer.
Prior to the development of the IDDSI Framework, other descriptors were used for food textures. Many organizations have not yet adopted the new terminologies and adhere to the old nomenclature. The state of Connecticut, Department of Developmental Services, using the old terminology has published Guidelines for Consistency Modifications of Foods and Liquids, which provides clear photographs of the different levels of food modifications. The photographs appear at the end of each section of the document and may be of help to someone who is modifying food texture for the first time.
Knowing what level of food texture modification is necessary for an individual is sometimes difficult because of the complexities of all the steps involved in chewing and swallowing, and also the changes that take place in food consistency as it is chewed and mixed with saliva. For example, peanut butter changes from a solid to a liquid once it is in the mouth. Catriona Steele, et al., conducted a systematic review of research that has been conducted in this area which is titled: The Influence of Food Texture and Liquid Consistency Modification on Swallowing Physiology and Function: A Systematic Review. Their report provides insight into the range of issues that must be considered to fully understand the impact of making these changes.
Regardless of the texture of food that is prescribed, the Mealtime Partner Dining System is able to serve it. Therefore, individuals who have difficulty feeding themselves are able to eat independently even if they consume a texture modified diet.
| The Drink-Partner Drinking System | |
| The Drink-Partner Drinking System is a hands-free drinking system that can be attached to a wheelchair or bed and allows independent access to water, or other drinks, for those who have little or no hand, or arm function. It consists of a cup holder and a bottle. The bottle has a flexible tube attached to its cap that holds the drinking straw and allows the straw to be position close to the user’s lips. | |
 |
 |
| Drink-Partner Drinking System (6040) |
Drink-Partner Drinking System for Slide-Track (6050) |
| Two different mounting systems are available for the cup holder: Part 6040 – The Drink-Partner Drinking System, attaches to a wheelchair handle or frame or a bed rail. Part 6050 – The Drink-Partner Drinking System for Slide-Track can be mounted on the slide-track rails of many powered wheelchair. (It comes with a hex wrench to make mounting easy.) | |
| --------------------------------------------------------------------- | |
| For more information about all of the Mealtime Partners assistive drinking systems, click here. Or, to speak with a company representative, please call us 800-996-8607. | |
As we age our ability to chew sometimes becomes impaired. It is quite difficult, and time consuming, for a speech pathologist to analyze the exact chewing and swallowing abilities of their patients. This makes it difficult to determine the exact modification that should be made to food texture to accommodate safe chewing and swallowing. Shinichi Wada and colleges in the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, at Showa University School of Medicine, Tokyo, recently conducted a study to evaluate the use of color-changeable chewing gum in evaluating chewing performance: “What Type of Food Can Older Adults Masticate?: Evaluation of Mastication Performance Using Color-Changeable Chewing Gum.”
The study included 30 participants who chewed gum for two minutes before spitting it out. As the gum was chewed, depending upon the participant’s mastication abilities, it changed color from yellowish green to various shades of red. The color change indicated the participant’s proficiency in chewing. The photograph below shows the gum in its wrapper with the color scale for assessing the level of proficiency in chewing on the side of it. The left bottom of the picture shows the gum before it is chewed and to the right is a piece of gum that has been chewed.
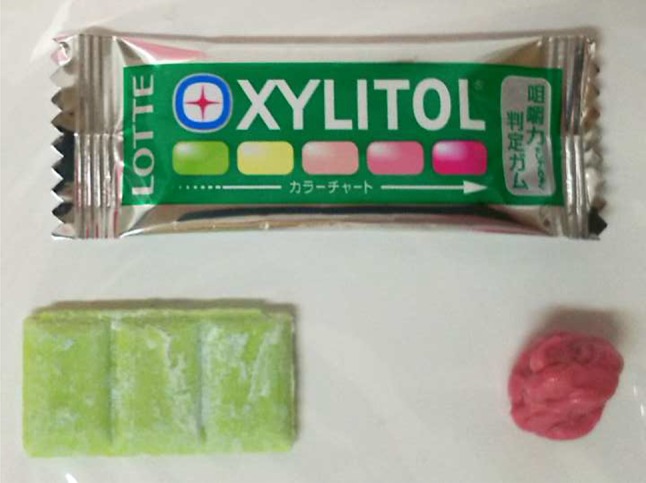

To measure the reliability of the chewing gum assessment, the researchers conducted chewing assessment using 5 different regular foods: boiled fish-paste, rice cracker, fried pork, boiled rice, and white bread, to compare with the chewing gum assessment. Food texture properties of hardness, cohesiveness, and adherence were measured. Participants chewed a mouthful of food until they were ready to swallow it. At that time they spit it out. The weight of the food before it was put into the mouth, the frequency of chewing, length of time food was chewed, and the texture of the food after chewing were all measured. The white bread, included in the study, was found to be too adhesive and not suitable for the study.
The remaining four foods provided similar findings about the participants ability to chew that were found from the chewing gum evaluations. The study conclusion was that using color-changeable chewing gum to assess mastication ability in older adults was an effective method of quickly and easily deciding what texture modification would be appropriate for an individual who may have chewing and swallowing difficulties.
This article provides only a brief overview of this interesting research. To read the complete article use the following link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5608775/
|
Did You Know? Did you know that according to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) this flu season is predicted to be the worst we have experienced in many years? The actual figures will not be known until later this year. The greatest increase seems to be occurring due to the H3N2 strain of the flu virus. This year’s flu vaccine is not very effective against H3N2 and for young children, infants, and older people the strain can be serious. Even though this year’s flu vaccine is not very effective, people, especially those at high risk who have not yet had a flu shot, should do so as soon as possible. The flu shot can lessen the effects of the virus and shorten how long it lasts. CDC recommendations for avoiding catching the flu include washing your hands frequently; keep your hands away from your eyes, nose and mouth; avoiding people who are sick; covering your mouth when you cough and drink plenty of fluids. They recommend that if you catch the flu, you should take an antiviral medication, like Tamiflu, as soon as possible once the flu is contracted. Because of the number of people who are sick, hospital waiting rooms are overflowing. It is recommended that rather than going to the hospital, if you are sick, you see your physician, or go to an urgent care center. If you are having trouble breathing or have a fever that is not controlled by taking Tylenol, you should definitely contact your doctor. |
To subscribe to the Mealtime Partners Newsletters, click here.
Mealtime Partners Website Navigation:
Home | Dining | Drinking | All Products | Ordering | Training | Calendar | FAQ | Newsletters | Contact
Please send comments and suggestions to newsletters@mealtimepartners.com
Copyright © Mealtime Partners, Inc. 2018
All rights reserved.